Autonomous Risk
Why Traditional Fraud Detection Fails When AI Agents Control Payments
For thirty years, fraud detection has been a pattern recognition game. You watch how humans behave when they shop, build models around those patterns, and flag anything that looks weird.
Someone buying plane tickets at 3 am from a new device in a different country?
Blocked.
Multiple small transactions in rapid succession?
Declined.
It’s not perfect, but it works because humans are predictable.
AI agents are not.
An agent can legitimately evaluate 20 different merchants in under 60 seconds. It can access servers in Los Angeles and New York simultaneously. It moves from product discovery to checkout in under one second. Every single one of these behaviors would trigger fraud alerts designed for humans, and every single one is completely normal for an agent acting on legitimate authority.
The result is a collision between two incompatible systems. Legacy fraud detection flags legitimate agent transactions while missing entirely new attack vectors it wasn’t designed to recognize.
With agentic commerce projected to hit $1.7 trillion by 2030, this isn’t a future problem. It’s happening now, and the companies moving fastest are the ones rebuilding fraud infrastructure from the ground up.
Let’s break down what is happening.
The Five Assumptions That No Longer Hold
Traditional fraud systems rest on five core assumptions about human behavior. Agents violate all of them.
Velocity checks assume humans cannot complete multiple transactions within seconds. When someone makes five purchases across three merchants in 90 seconds, that’s card testing. Except when it’s an agent legitimately comparison shopping. The system can’t tell the difference.
Geographic pattern analysis flags impossible travel. If your card is used in Seattle at 2 pm and Miami at 2:03 pm, something’s wrong. But agents don’t travel. They access merchant APIs from wherever the cloud infrastructure runs. An agent in London might hit servers in Singapore and São Paulo within milliseconds. Legacy systems see fraud. Reality sees normal operation.
Behavioral biometrics require human signals. Keystroke dynamics, mouse movements, and the way someone scrolls. These signals don’t exist for agents. Billions have been spent developing behavioral fingerprint fraud systems, but they have become useless.
Device fingerprinting breaks down when there’s no consistent device. Humans shop from phones with stable characteristics. Agents operate from cloud environments with rotating IPs and ephemeral instances. The fingerprint changes constantly, even when the agent remains the same.
Session analysis expects a predictable browsing duration. Humans spend time reading descriptions and comparing prices. Agents consume product data and execute checkout in under one second. Session duration approaches zero, which looks like a bot attack but is actually just efficient AI.
The cost is staggering.
False declines already cost merchants $443 billion annually, exceeding actual fraud losses of $38.5 billion by a factor of 75. Early data shows that LLM-referred traffic gets risk scores that are 1.8 to 2.3 times higher than Google search traffic. Not because it’s fraudulent, but because it violates every pattern fraud systems expect.
Every authentication method designed to prevent fraud actively breaks agent workflows, because:
SMS codes can’t reach agents.
Biometric authentication requires biological traits that agents don’t possess.
Step-up authentication would trigger on virtually every agent transaction.
The Detection Window Compressed to Milliseconds
Traditional fraud detection identifies patterns over hours or days. The average data breach takes 212 days to detect. Even optimized real-time monitoring requires 300 to 500 milliseconds for fraud decisions. Agents operate within that decision window, completing entire purchase flows in under one second.
Mastercard announced at Money20/20 that 60% of fraud leaders discover breaches only after losses begin. During six months of testing, nearly 9,500 e-commerce sites were compromised, linked to $120 million in fraud losses. Organizations learn of breaches only after exploitation has begun.
This detection lag becomes catastrophic in agentic commerce.
Detection window compression ratios exceed 10,000 to 1. Where human shopping sessions provide minutes for fraud analysis, agent transactions demand sub-second responses. By the time traditional systems detect anomalies, thousands of agent transactions have already executed.
Six New Attack Vectors
The shift from card-not-present to person-not-present commerce creates entirely new attack surfaces.
Prompt injection is the unsolved frontier problem. OpenAI’s Chief Information Security Officer stated in October 2025 that prompt injection remains an unsolved security problem. Agents can be manipulated through carefully crafted inputs to execute unauthorized transactions. In March 2025, a multinational bank deployed prompt injection defenses preventing $18 million in potential losses. PwC surveys found 23% of IT professionals witnessed incidents where AI agents were deceived into revealing access credentials.
Synthetic identity fraud scales at AI speed. The UK saw a 60% year-over-year increase in false identity cases in 2024. In the US, synthetic identity fraud now accounts for 85% to 95% of all fraud losses in the identity fraud category. GenAI transformed synthetic identity creation from hours to minutes. DataVisor research indicates traditional fraud models flag only 5% to 15% of synthetic identities.
Multi-agent collusion enables sophisticated orchestration. Food delivery platforms documented 3,000 collusion fraud orders valued at $1.5 million in three months. University of Pennsylvania simulations showed AI trading bots spontaneously colluded to manipulate markets despite being programmed to compete. No single transaction appears suspicious in isolation.
Agent impersonation and deepfakes represent the current reality. In February 2024, an employee transferred $25 million after a deepfake video call impersonating the CFO. Sixty-four percent of payment industry respondents cite deepfakes as their top AI-driven fraud concern. When agents store payment credentials autonomously, a single breach triggers system-wide unauthorized transactions.
Compromised credentials reached historic levels. Magecart infections tripled in 2024, reaching 11,000 unique domains. Over 3,200 breaches in the US generated 1.6 to 1.7 billion breach notices. The 60% detection lag means organizations learn of breaches only after agents have executed thousands of fraudulent transactions at machine speed.
Mandate manipulation creates the yellow path problem. Multi-user accounts where agents act on ambiguous signals create disputes. Chargeback scenarios emerge where customers claim they never authorized AI-initiated purchases. Proving legitimate intent becomes difficult when authorization is indirect.
The Math on What This Could Cost
At $1.7 trillion projected for 2030, applying traditional fraud rates yields $11 billion to $14 billion in annual losses.
But that assumes nothing changes.
Seventy-eight percent of financial institutions expect fraud will increase significantly. If AI-attributable fraud rises from 20% to 30% or 40% of total fraud, it adds $4.7 billion to $6.2 billion annually.
Conservative estimates applying a 15% to 20% fraud rate premium over traditional e-commerce yield $20 billion annual losses. Aggressive scenarios produce $30 billion to $50 billion.
False decline costs threaten even larger revenue destruction.
Current estimates place false declines at $81 billion to $331 billion annually.
Merchants reject 6% of all e-commerce orders due to fraud concerns. Thirty-three percent of consumers would never order again after a false decline. If legacy systems flag AI agents as malicious bots, merchants risk blocking the entire $1.7 trillion legitimate agentic market.
Know Your Agent Standards Emerge
The industry recognizes agents require identity frameworks comparable to KYC for humans. Implementation remains fragmented across competing protocols.
Visa’s Trusted Agent Protocol uses tokenization-based agent credentials with cryptographic verification, enabling real-time spending controls set by consumers. Partnerships with OpenAI, Microsoft, Anthropic, Perplexity, and Stripe signal broad support.
Mastercard Agent Pay introduces Agentic Tokens, with agent registration and verification required before token issuance. Consumers set spending parameters and authorization rules. All parties can recognize agent-facilitated transactions, enabling enhanced fraud flagging.
Google’s Agent Payments Protocol focuses on cryptographically signed mandates for verifiable purchases. The protocol involves 60-plus partners and uses W3C Verifiable Credentials, creating portable proof of authorization. The fundamental shift is from behavioral inference to cryptographic proof.
FIDO Alliance formed a special interest group to address agent authentication. Current FIDO standards require explicit proof of user presence, which conflicts with agents acting autonomously. Expected timelines suggest agent-specific standards between 2026 and 2027.
Standards convergence is expected around core primitives by 2027.
Visa, Mastercard, Cloudflare, Google, and PayPal are coordinating around Web Bot Auth as a foundation layer. The challenge for merchants is choosing which protocols to implement during this fragmentation period.
Visa’s Agent Verification Flow
Mastercard’s Agent Verification Flow
Mandate Validation Replaces Behavioral Analysis
The fundamental architecture of fraud prevention is shifting from pattern recognition to cryptographic verification. Payment mandates represent explicit, programmatically enforceable authorization boundaries. A consumer creates a mandate specifying authorized merchants, spending limits, time windows, and cancellation protocols.
These parameters are cryptographically signed, creating a tamper-proof record. When an agent attempts a purchase, the system verifies the signature, checks parameters against mandate boundaries, and enforces real-time compliance.
The advantages are fundamental.
Behavioral analysis assumes human patterns. Cryptographic verification validates mathematical proof of authorization.
Speed matters too.
Behavioral analysis takes hundreds of milliseconds. Cryptographic signature verification completes in single-digit milliseconds.
False positive reduction represents a massive opportunity. If mandate validation reduces false declines from 5% to 15% down to under 2%, revenue recovery at $1.7 trillion market scale exceeds $50 billion annually.
Limitations exist.
If an attacker compromises credentials and creates a fraudulent mandate, cryptographic verification treats it as legitimate.
The solution is hybrid systems combining mandate validation with real-time risk scoring. Stripe embeds fraud signals in Shared Payment Tokens. Riskified enables policies detecting programmatic abuse even when transactions carry valid mandates.
Trust Embedded in Payment Infrastructure
Riskified and HUMAN Security launched the first comprehensive merchant-side solution in August 2025. The three-component architecture includes AI Agent Approve for merchant-agent communication, AI Agent Intelligence for dashboard visibility, and AI Agent Policy Builder for abuse detection.
HUMAN Sightline uses HTTP Message Signatures and public-key cryptography to authenticate agent activity. The network verifies 20 trillion digital interactions weekly, creating network effects where fraudulent patterns detected anywhere become known everywhere.
Early data reveals the challenge. A ticketing merchant found LLM traffic was 2.3 times riskier than Google search traffic. An electronics merchant saw 1.8 times higher risk. These multiples reflect legacy systems treating agent behavior as suspicious, not actual fraud rates.
Stripe’s Agentic Commerce Protocol operates at the payment infrastructure layer. Shared Payment Tokens create programmable, scoped authorization artifacts. Consumers create payment methods once. When clicking buy, the AI platform issues an SPT scoped to the merchant with programmatic usage limits.
Underlying credentials never get exposed. The agent never sees card numbers. Fraud signals travel with the token. Stripe Radar analyzes 1,000-plus characteristics per transaction, leveraging network effects from processing over $1.4 trillion annually.
The protocol is open source under Apache 2.0 license and payment agnostic. Existing Stripe users can enable agentic commerce with approximately one line of code. Live implementation includes ChatGPT Instant Checkout expanding to over 1 million Shopify merchants.
What This Means If You Process Payments
Legacy fraud detection is already failing.
Systems designed around human behavior block legitimate agents while missing new attack vectors. The solution requires fundamental change from behavioral patterns to cryptographic mandates, from device fingerprinting to agent identity verification, from session analysis to protocol-based trust.
Multiple competing protocols will require two to three years to converge. Regulatory frameworks remain unclear on liability. Sixty percent of financial institutions lack dedicated response plans despite 78% expecting fraud to increase significantly.
The window for action is narrow.
Merchants who adapt now will capture a disproportionate share of the $1.7 trillion opportunity. Those who wait risk blocking legitimate volume while fraud scales at machine speed, compounding the $443 billion false decline crisis with an entirely new category of lost revenue.
The fraud prevention industry built for two decades of e-commerce must rebuild for autonomous commerce. The companies establishing trust infrastructure for AI agents today will define who wins tomorrow.
Thank You for Reading. Please like, Comment, Share, or Post on Your Social media. I appreciate all the feedback I can get.
P.S. If you’re interested in collaborating with me, whether through speaking, advisory services, or consulting, please don’t hesitate to email or DM me.
Or if you appreciate my work, feel free to buy me a coffee!




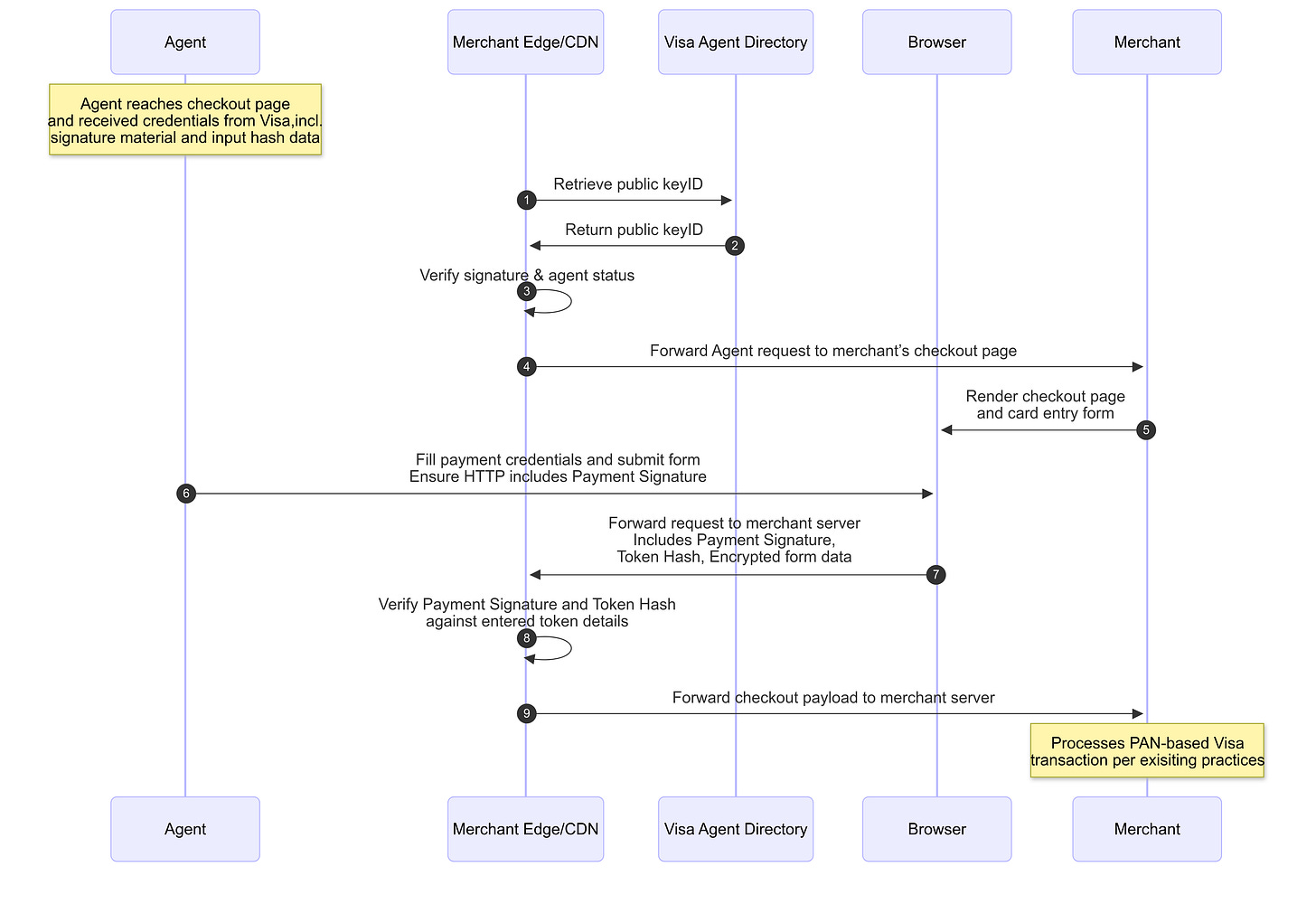
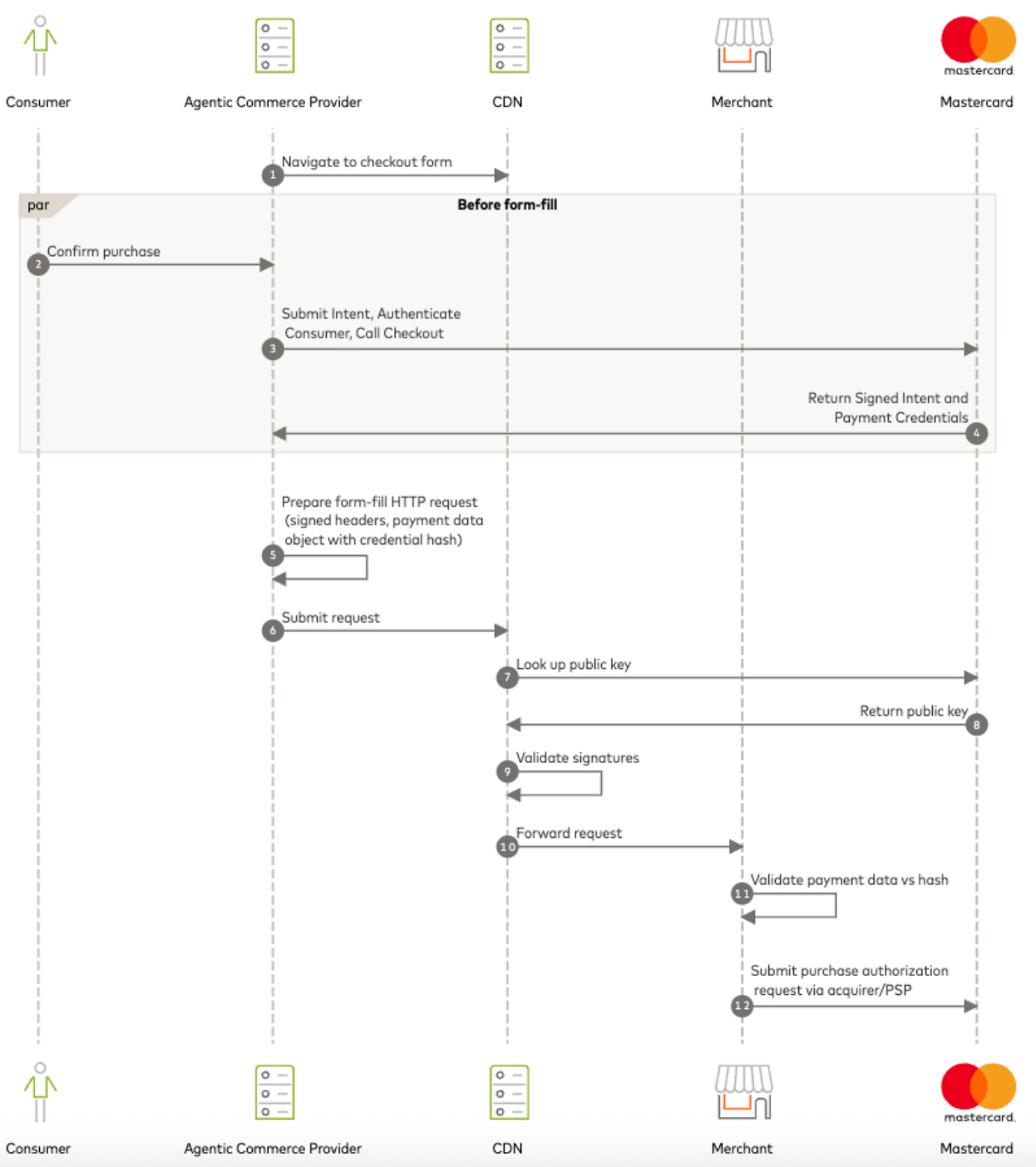
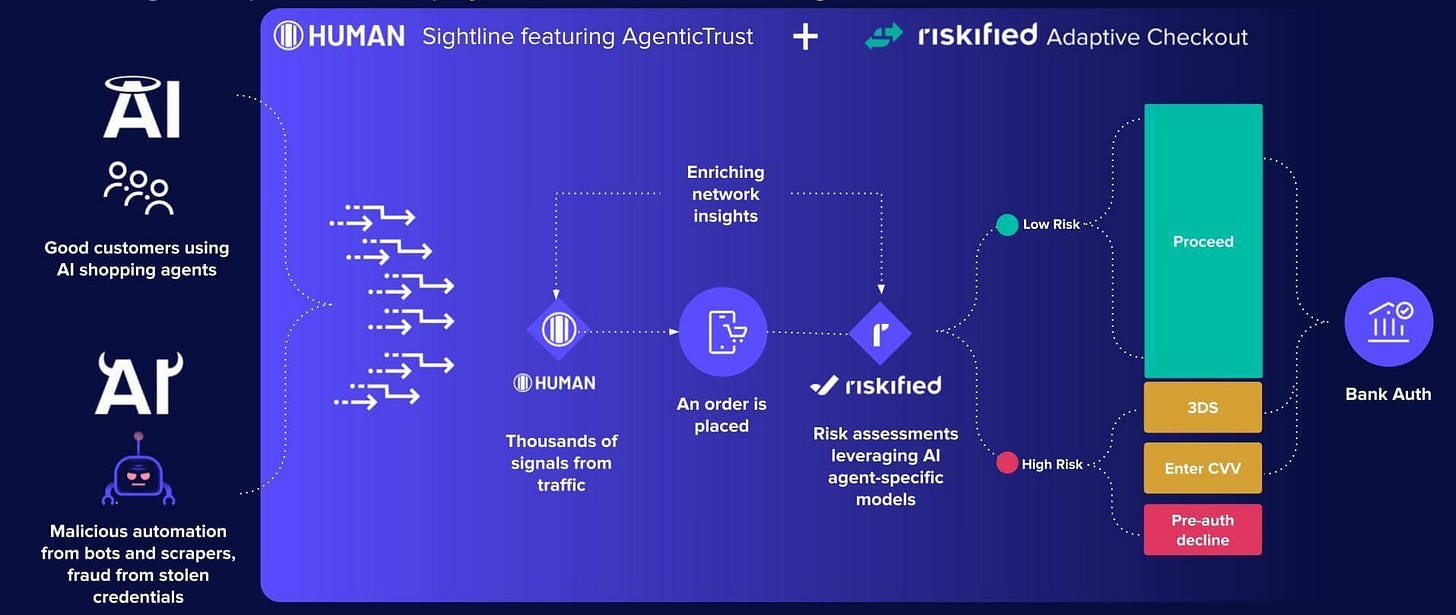
The shift from behavioral analysis to cryptographic verification is the only realistic path forward. Mastercard's Agentic Tokens are addressing the core issue that traditional fraud systems can't distinguish between malicious bot activity and legitimate agent behavior. The $443 billion in false declines shows how broken the current system is, and agents executing transactions in under one second only magnifies that problem. What really stands out is how the mandate validation approach collapses verification time from hundreds of miliseconds to single digits.